A steady stream of investment has driven tremendous growth in subsea cable infrastructure to keep pace with ever-increasing bandwidth demand.
According to new data from TeleGeography’s Transport Networks Research Service, the aggregate cost of new construction over the past nine years has averaged over $2 billion annually.
Let’s review the state of submarine cable investment in 2025.
Meeting Demand Requirements in 2025
With the exception of a few anomalous years, we haven’t seen this level of investment in subsea cable infrastructure since 2000-2001, and it’s not letting up. The value of new submarine cables planned to enter service between 2025 and 2027 is forecasted to reach over $13 billion.
Construction Cost of Submarine Cables
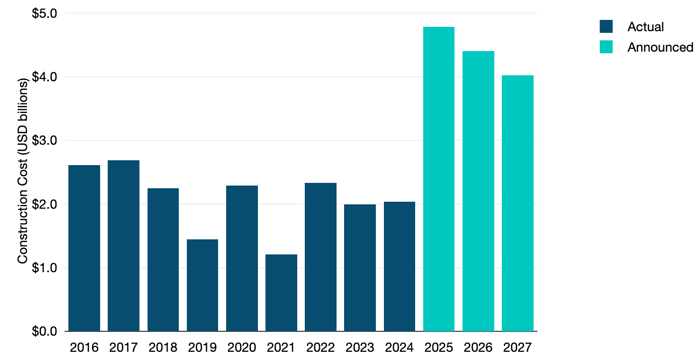
Notes: Total construction costs of all international and domestic submarine cables entering service in designated years. Construction costs exclude the cost of subsequent capacity upgrades and annual operational costs. 2025-2027 construction costs based on announced contract values and TeleGeography estimates. Not all planned cables may be constructed.
How is this substantial investment in subsea infrastructure being deployed regionally? In the past three years, no single route stands, although intra-Asian routes have had the most extensive investment with $1.2 billion in new cables, and Latin American routes have seen the least with about $200 million in new investment.
Look at the coming three years in the chart below. We see a significant surge in new cable investment across every route we track.
The biggest surge is expected in the trans-Pacific, where multiple Google and Meta-led cables, along with several others, will drive an aggregate of over $3 billion in spending.
Construction Cost of New Submarine Cables Entering Service by Region
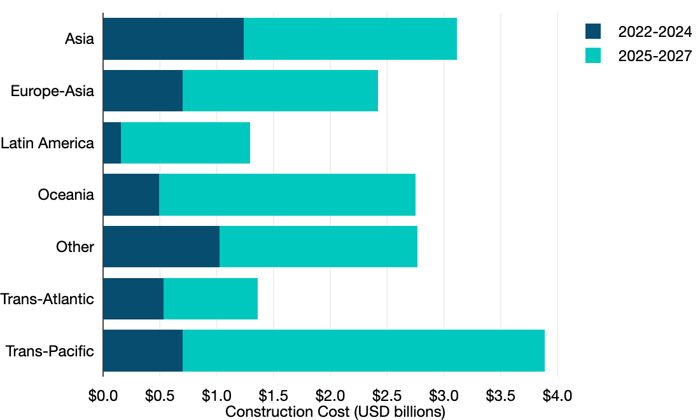
Notes: Construction costs based on the year the cable entered service. Construction costs exclude the cost of subsequent capacity upgrades and annual operating costs. 2025-2027 construction costs based on announced contract values and TeleGeography estimates. Not all planned cables may be constructed.
Source: © 2025 TeleGeography
Reasons for New Submarine Cables
There are numerous reasons for the surge in new cables around the world. Here are a few influential factors:
- Scarcity of potential capacity and fiber pairs. The most fundamental driver for new cable construction is the limited availability of potential capacity. Demand continues to rise at an exponential rate and could soon lead to capacity exhaustion without new cable investment.
- Ownership economics. Content providers are the largest users of bandwidth. As their scale rises on a route, they eventually become reluctant to lease wavelengths or purchase wavelength IRUs on existing cables. Instead, content providers with sufficient demand have begun acquiring capacity at cost by investing in new cables.
- Route diversity. Consumers of submarine cable capacity purchase bandwidth on multiple cable systems. Creating mesh networks is important to provide a high level of network availability.
- Reducing equipment costs. As their bandwidth requirements continue to surge, operators are concerned with the cost of adding capacity. By building new cables with massive capacities, network operators can achieve lower unit costs compared to lower-capacity legacy cables.
- Replacing aging cables. The need for new cables is also related to the expected retirement of aging cables.
Download the new Transport Networks Executive Summary to keep reading our latest analysis on the state of global network infrastructure.


